TILES
The TILE ecosystem has been designed to address the multitude of obstacles that have continued to hold back the rapid development and deployment of embedded intelligent systems. Our aim, put simply, is to do for embedded electronics what 3D printing has done for mechanical design, prototyping, and production. To achieve this vision, tiles aim to
removing the barriers to access for cutting-edge technology
modern sensors, processors, and functional ICs continue to shrink into domains that become ever more difficult to design, fabricate, and realize
modularize and reduce system complexity
each TILE includes all of the necessary components to fulfill its functional purpose and interact with other systems.
work at a human-scale
TILEs are designed to strike the perfect balance between miniaturization and easy of use/access.
cover the full domain
as can be seen in the constantly-evolving library below, tiles are being developed to cover the full range of embedded-systems needs, from processing and power management to sensing, actuation, communication, and more.
standalone capable
while TILEs are best used in combinations, they can just as easily be integrated into third-party systems to solve particular needs.
code support
we have a growing library of open-source drivers and starter code.
STANDARDS
PACKAGING
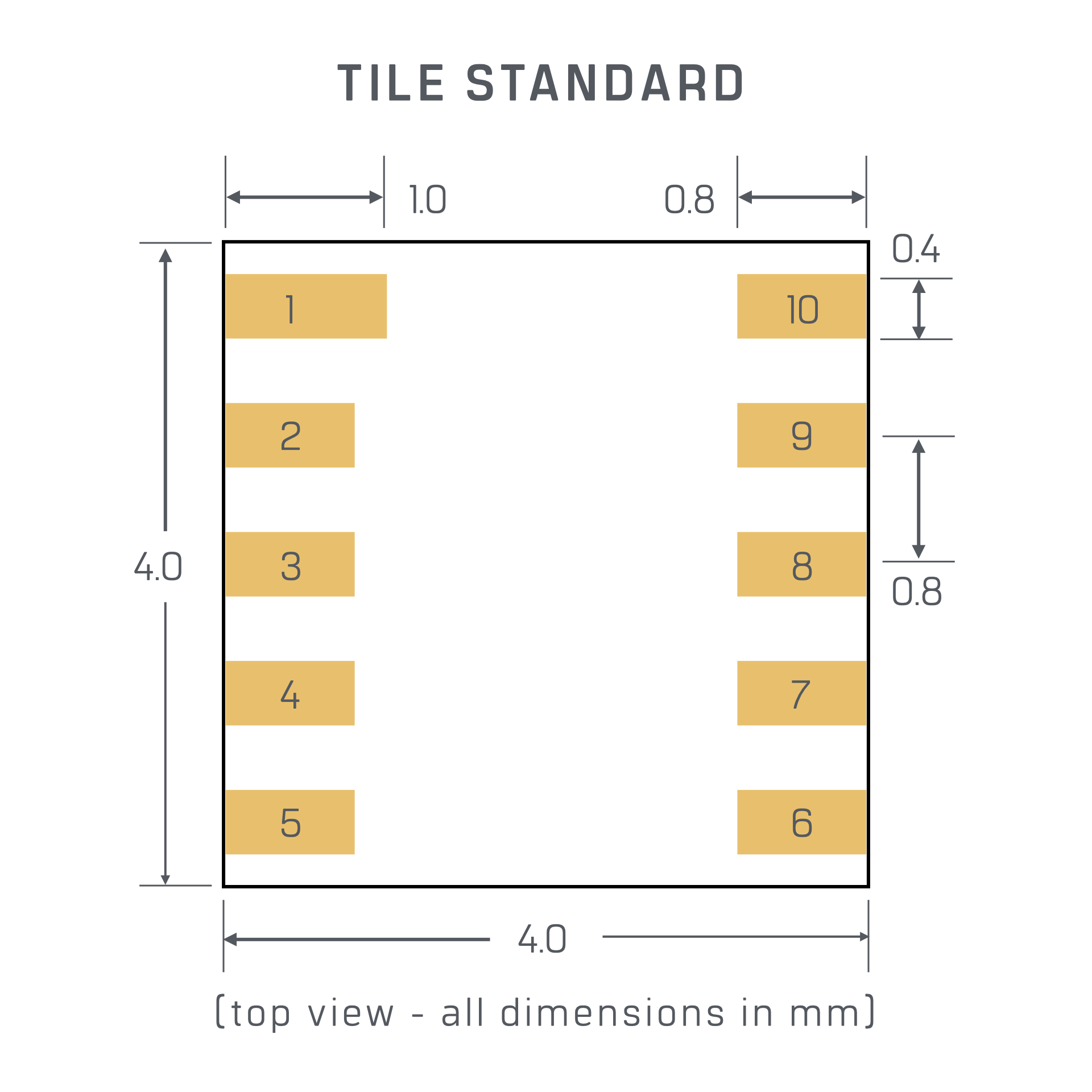
Most tiles fit into the standard “T44-10” 4.0 x 4.0 mm package with two rows of 0.4mm wide, 0.8mm pitch solder pads on the bottom surface (with pad 1 being 0.2mm longer than the others). Deviations from this standard are noted by changes in the board dimensions (T48, T88, etc.) or the number of pads (-12, -22, etc.), as commonly found in the CORE family for added I/O or programming.
PAD ASSIGNMENTS
With a few exceptions, the tiles adhere to the following standard pad assignments:
1 - SUPPLY GND
2 - SPI.MISO
3 = SPI.CS
4 = I2C.CLK / SPI.CLK
5 = I2C.DAT / SPI.MOSI
10 = SUPPLY V+
Our portfolio currently contains 6 tiles in production, 5 staged for release, 18 in the prototype-validation phase, and 26 under active development. For further details, please open the library below.